Besides using a debugger (e.g. gdb) with the debug build (see below), the SUMO source code offers debugging macros at several locations, which are usually deactivated (e.g., commented out). Activating the macros can yield a detailed program output, that can be configured by given parameters.
Debug Build#
To create debugging symbols during the build, see the build instructions
for your operating system (Linux /
Windows /
macOS). The corresponding binaries
receive the suffix D (e.g. sumoD instead of sumo). The debug
configuration defines a preprocessor macro _DEBUG that may be used to
encapsulate debug specific code. For simple text debugging, local macros
should be used that can be switched on and off more flexibly, see below.
Local Debug Macros#
The recommended style for inserting reusable debugging code in SUMO is
encapsulation by preprocessor directives. This is done by placing a
#define DEBUG_THIS_CODE at the beginning of a source (preferably just
below any other #include or #define macros). The debugging code
(e.g. some output to std::cout) should then be surrounded by
#ifdef DEBUG_THIS_CODE
...
#endif
Thus, it can be switched on and off by (un)commenting the
#define DEBUG_THIS_CODE line.
Sometimes it is useful to combine this with a condition for more specific debugging output. For instance, if only output for the vehicle with ID 'my_new_ferrari' is needed while looping through all vehicles, you should insert a corresponding debug condition
#define DEBUG_COND (veh.getID() == "my_new_ferrari")
(at the same location as the #define DEBUG_THIS_CODE) and encapsulate
the debug code further as
#ifdef DEBUG_THIS_CODE
if DEBUG_COND {
...
}
#endif
Note that this presupposes that veh is a reference to the current
vehicle, which is being looped over. It is worth mentioning that you can
also define debug conditions with arguments to become a bit more
flexible. For example:
#define DEBUG_COND(x) (x != 0 && x->getID() == "my_new_ferrari")
...
#ifdef DEBUG_THIS_CODE
if DEBUG_COND(veh_pointer) {
...
}
#endif
Debugging macros already exist at several locations (see some of these before implementing your own):
- src/microsim/MSLane.cpp
- src/microsim/MSLink.cpp
- src/microsim/MSVehicle.cpp
- src/microsim/lcmodel/MSLCM_LC2013.cpp
- src/guisim/GUIVehicle.cpp
- src/guisim/GUILane.cpp
Selection based vehicle debugging#
The header utils/common/StdDefs.h provides the String
gDebugSelectedVehicle, which always holds the id of the last vehicle,
which was selected in the GUI, and can be used in the debugging
conditions to obtain a dynamic debugging selection (provided the
corresponding macro is activated).
Debugging external libraries#
Debugging symbols (.pdb files) are available for some of the external libraries included in SUMOLibraries. To use them in Visual Studio, simply add the path of the desired symbol to the "Symbol file locations" in the Options menu. Do so by going to Tools > Options... > Debugging > Symbols and adding the path to the .pdb file of the desired external library as a new location (see the example image below). The .pdb files are usually located in the lib or bin directory, for each library.
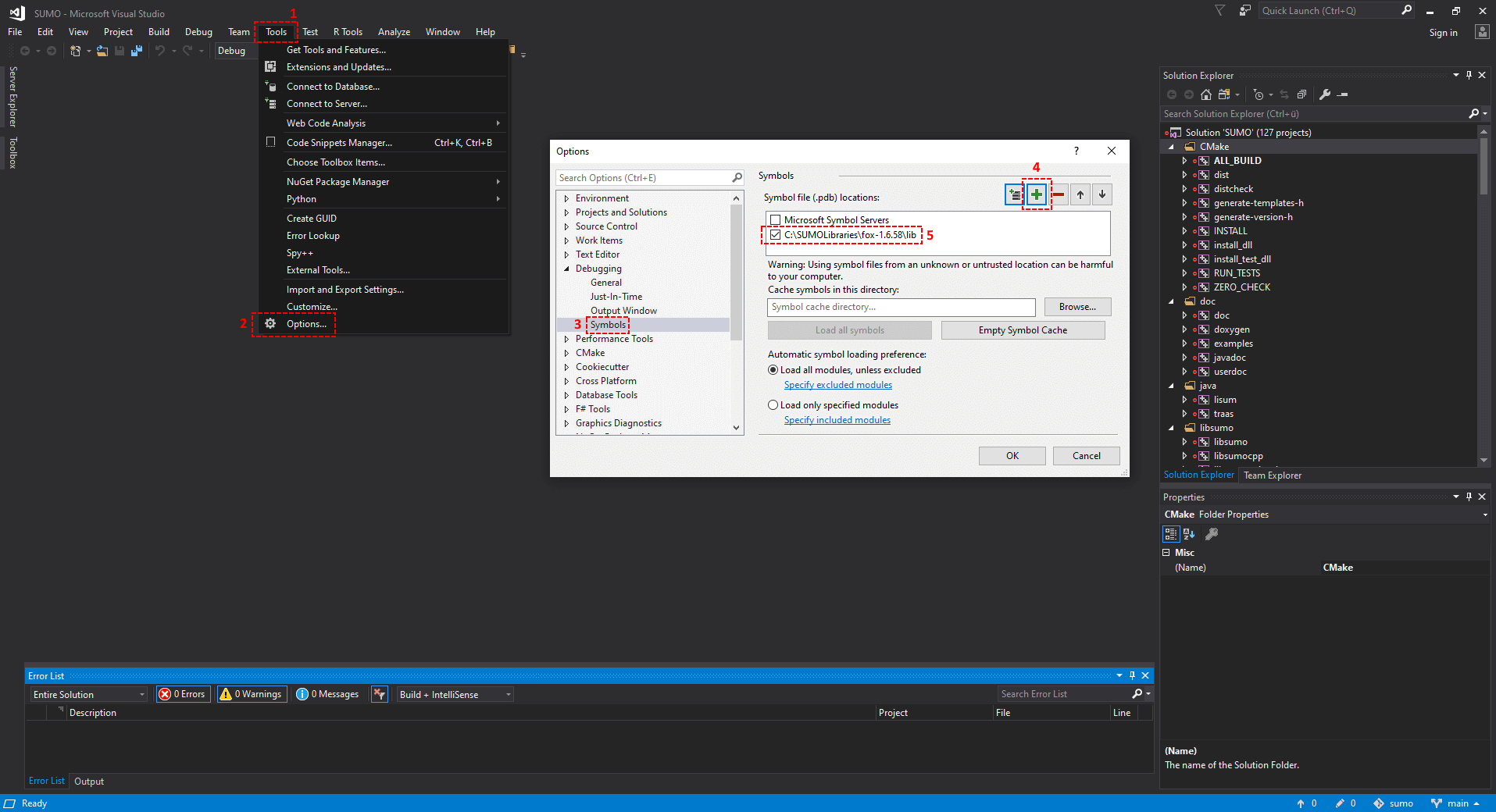
Example: Adding the FOX debugging symbol
FOX Toolkit message logging#
The FOX Toolkit library uses a macro to output debugging messages of varying importance. Every message gets a numeric level assigned and will get printed only in debug mode. In order to receive the messages, it is necessary to provide the command line parameter -tracelevel <INT> to sumo-guiD. Only messages with an assigned level below the given level will be printed to the console.

